目标检测-CPU训练NanoDet-plus自己的数据集
NanoDet是一种轻量化模型,速度快并且适合部署在端侧,不过因为模型对于新版本torch和CUDA不太适配(torch>=1.10,
前言
NanoDet是一种轻量化模型,速度快并且适合部署在端侧,不过因为是近几年较新的模型对于新版本torch和CUDA不太适配(torch>=1.10,<2.0),加上CUDA配置比较麻烦,笔者已有版本较高,因此使用CPU来训练NanoDet,在此总结了数据集配置和训练的笔记以及踩过的坑帮助快速上手。
NanoDet的GitHub网址:https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet
对原理感兴趣的伙伴可以阅读作者自己写的知乎介绍:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/306530300
一、数据集配置
大致思路:先对数据进行标注生成原始图片、标签数据,划分训练集与测试集,进行数据增强。
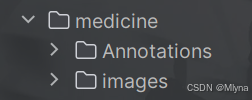
1、VOC数据集制作
NanoDet支持VOC与COCO数据集,这里使用后者,先配置VOC数据集格式之后会进行转化,使用labelimg进行数据标注任务,具体操作可见大佬的分享:目标检测---利用labelimg制作自己的深度学习目标检测数据集-CSDN博客
(标注时小心操作,因为保存按钮和格式切换按钮离得近,之前打标签时不小心点到格式转换使得标签文件夹下存在两种格式数据,笔者又重新标注了一遍,小心为好。)
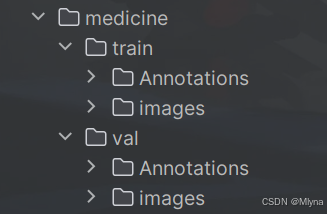
2、划分数据集
对数据集进行训练集和验证集的划分,方便后续操作,代码如下:
# 图片和标签划分为训练集、测试集
import os
import shutil
import random
# 设置原始数据集、训练集和验证集的路径
images_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
annotations_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
train_images_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
val_images_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
train_annotations_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
val_annotations_dir = "YOUR_FILE_PATH"
os.makedirs(train_images_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_images_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(train_annotations_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_annotations_dir, exist_ok=True)
images = [f for f in os.listdir(images_dir) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(images_dir, f))]
annotations = [f for f in os.listdir(annotations_dir) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(annotations_dir, f))]
# 确保图片和标签文件数量相同
assert len(images) == len(annotations), "图片和标签文件数量不匹配"
# 随机打乱,分割数据集
indices = list(range(len(images)))
random.shuffle(indices)
split_point = int(len(images) * 0.8)
train_indices = indices[:split_point]
val_indices = indices[split_point:]
# 复制文件到训练集和验证集
for idx in train_indices:
img_name = images[idx]
ann_name = annotations[idx]
shutil.copy(os.path.join(images_dir, img_name), train_images_dir)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(annotations_dir, ann_name), train_annotations_dir)
for idx in val_indices:
img_name = images[idx]
ann_name = annotations[idx]
shutil.copy(os.path.join(images_dir, img_name), val_images_dir)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(annotations_dir, ann_name), val_annotations_dir)
print("数据集划分完成。")运行代码后原始数据集会按照比例分为训练集和测试集
3、数据增强
对数据进行增强,可以帮助改善模型的训练效果,特别是在如图像分类、目标检测和图像分割等计算机视觉任务中。图像增强可以提高模型的泛化能力,减少过拟合的风险。如果你的数据集量充足且复杂可以省略,笔者原始数据集较少所以进行了增强操作。
这里使用imgaug库来增强数据,这是一个开源的Python库,提供了大量的图像增强技术,包括但不限于:
- 几何变换(如缩放、旋转、平移、裁剪、透视变换等)。
- 颜色变换(如亮度、对比度、饱和度、色调调整等)。
- 噪声注入(如高斯噪声、斑点噪声、椒盐噪声等)。
- 模糊效果(如高斯模糊、平均模糊、中值模糊等)。
- 边缘检测。
- 直方图变换。
具体代码如下:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import getcwd
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import shutil
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import imgaug as ia
from imgaug import augmenters as iaa
ia.seed(1)
def read_xml_annotation(root, image_id):
in_file = open(os.path.join(root, image_id))
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
bndboxlist = []
for object in root.findall('object'): # 找到root节点下的所有country节点
bndbox = object.find('bndbox') # 子节点下节点rank的值
xmin = int(bndbox.find('xmin').text)
xmax = int(bndbox.find('xmax').text)
ymin = int(bndbox.find('ymin').text)
ymax = int(bndbox.find('ymax').text)
# print(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)
bndboxlist.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
# print(bndboxlist)
bndbox = root.find('object').find('bndbox')
return bndboxlist
# (506.0000, 330.0000, 528.0000, 348.0000) -> (520.4747, 381.5080, 540.5596, 398.6603)
def change_xml_annotation(root, image_id, new_target):
new_xmin = new_target[0]
new_ymin = new_target[1]
new_xmax = new_target[2]
new_ymax = new_target[3]
in_file = open(os.path.join(root, str(image_id) + '.xml')) # 这里root分别由两个意思
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
xmlroot = tree.getroot()
object = xmlroot.find('object')
bndbox = object.find('bndbox')
xmin = bndbox.find('xmin')
xmin.text = str(new_xmin)
ymin = bndbox.find('ymin')
ymin.text = str(new_ymin)
xmax = bndbox.find('xmax')
xmax.text = str(new_xmax)
ymax = bndbox.find('ymax')
ymax.text = str(new_ymax)
tree.write(os.path.join(root, str("%06d" % (str(id) + '.xml'))))
def change_xml_list_annotation(root, image_id, new_target, saveroot, id,img_name):
in_file = open(os.path.join(root, str(image_id) + '.xml')) # 这里root分别由两个意思
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
elem = tree.find('filename')
elem.text = (img_name + str("_%06d" % int(id)) + '.jpg')
xmlroot = tree.getroot()
index = 0
for object in xmlroot.findall('object'): # 找到root节点下的所有country节点
bndbox = object.find('bndbox') # 子节点下节点rank的值
# xmin = int(bndbox.find('xmin').text)
# xmax = int(bndbox.find('xmax').text)
# ymin = int(bndbox.find('ymin').text)
# ymax = int(bndbox.find('ymax').text)
new_xmin = new_target[index][0]
new_ymin = new_target[index][1]
new_xmax = new_target[index][2]
new_ymax = new_target[index][3]
xmin = bndbox.find('xmin')
xmin.text = str(new_xmin)
ymin = bndbox.find('ymin')
ymin.text = str(new_ymin)
xmax = bndbox.find('xmax')
xmax.text = str(new_xmax)
ymax = bndbox.find('ymax')
ymax.text = str(new_ymax)
index = index + 1
tree.write(os.path.join(saveroot, img_name + str("_%06d" % int(id)) + '.xml'))
def mkdir(path):
# 去除首位空格
path = path.strip()
# 去除尾部 \ 符号
path = path.rstrip("\\")
# 判断路径是否存在
# 存在 True
# 不存在 False
isExists = os.path.exists(path)
# 判断结果
if not isExists:
# 如果不存在则创建目录
# 创建目录操作函数
os.makedirs(path)
print(path + ' 创建成功')
return True
else:
# 如果目录存在则不创建,并提示目录已存在
print(path + ' 目录已存在')
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
IMG_DIR = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ### 原始数据集图像的路径
XML_DIR = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ### 原始xml文件的路径
# =============================================================================
AUG_XML_DIR = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ### 数据增强后的xml文件的保存路径
try:
shutil.rmtree(AUG_XML_DIR)
except FileNotFoundError as e:
a = 1
mkdir(AUG_XML_DIR)
# =============================================================================
AUG_IMG_DIR = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ### 数据增强后图片的保存路径
try:
shutil.rmtree(AUG_IMG_DIR)
except FileNotFoundError as e:
a = 1
mkdir(AUG_IMG_DIR)
AUGLOOP = 9 # 每张影像增强的数量(即增加几倍)
boxes_img_aug_list = []
new_bndbox = []
new_bndbox_list = []
# 影像增强
seq = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.Flipud(0.5), # vertically flip 20% of all images
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # 镜像
iaa.Multiply((1.2, 1.5)), # change brightness, doesn't affect BBs
iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0, 3.0)), # iaa.GaussianBlur(0.5),
iaa.Affine(
translate_px={"x": 15, "y": 15},
scale=(0.8, 0.95),
rotate=(-30, 30)
) # translate by 40/60px on x/y axis, and scale to 50-70%, affects BBs
])
for root, sub_folders, files in os.walk(XML_DIR):
for name in files:
print(name)
bndbox = read_xml_annotation(XML_DIR, name)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(XML_DIR, name), AUG_XML_DIR)
# 注意图像文件格式
shutil.copy(os.path.join(IMG_DIR, name[:-4] + '.jpg'), AUG_IMG_DIR)
for epoch in range(AUGLOOP):
seq_det = seq.to_deterministic() # 保持坐标和图像同步改变,而不是随机
# 读取图片
img = Image.open(os.path.join(IMG_DIR, name[:-4] + '.jpg'))
# sp = img.size
img = np.asarray(img)
# bndbox 坐标增强
for i in range(len(bndbox)):
bbs = ia.BoundingBoxesOnImage([
ia.BoundingBox(x1=bndbox[i][0], y1=bndbox[i][1], x2=bndbox[i][2], y2=bndbox[i][3]),
], shape=img.shape)
bbs_aug = seq_det.augment_bounding_boxes([bbs])[0]
boxes_img_aug_list.append(bbs_aug)
# new_bndbox_list:[[x1,y1,x2,y2],...[],[]]
n_x1 = int(max(1, min(img.shape[1], bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[0].x1)))
n_y1 = int(max(1, min(img.shape[0], bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[0].y1)))
n_x2 = int(max(1, min(img.shape[1], bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[0].x2)))
n_y2 = int(max(1, min(img.shape[0], bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[0].y2)))
if n_x1 == 1 and n_x1 == n_x2:
n_x2 += 1
if n_y1 == 1 and n_y2 == n_y1:
n_y2 += 1
if n_x1 >= n_x2 or n_y1 >= n_y2:
print('error', name)
new_bndbox_list.append([n_x1, n_y1, n_x2, n_y2])
# 存储变化后的图片
image_aug = seq_det.augment_images([img])[0]
path = os.path.join(AUG_IMG_DIR,
name[:-4] + str( "_%06d" % (epoch + 1)) + '.jpg')
image_auged = bbs.draw_on_image(image_aug, thickness=0)
Image.fromarray(image_auged).save(path)
# 存储变化后的XML
change_xml_list_annotation(XML_DIR, name[:-4], new_bndbox_list, AUG_XML_DIR,
epoch + 1,name[:-4])
print( name[:-4] + str( "_%06d" % (epoch + 1)) + '.jpg')
new_bndbox_list = []
注意更改的地方:需要对自己数据集路径进行修改,增强数量AUGLOOP视情况而定,同时考虑到图片格式,默认jpg,如果不是大概有五六处需要更改。
4、格式转换:VOC转COCO
运行脚本将刚刚配置好的VOC格式数据集转换为COCO格式,原先的VOC格式xml文件和图片一 一对应,转换后每张图片的标注信息统一在一个json文件中。分别运行训练集和测试集进行转换,成功运行后结果应该是生成两个json文件,每一个分别对应训练集、测试集Annotations文件夹里所有xml文件信息
代码如下:
# 将xml转化为json格式
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import json
coco = dict()
coco['images'] = []
coco['type'] = 'instances'
coco['annotations'] = []
coco['categories'] = []
category_set = dict()
image_set = set()
category_item_id = 0
# image_id = 'ball-'
image_id = 0
id_num = 0
annotation_id = 0
def addCatItem(name):
global category_item_id
category_item = dict()
category_item['supercategory'] = 'none'
category_item_id += 1
category_item['id'] = category_item_id
category_item['name'] = name
coco['categories'].append(category_item)
category_set[name] = category_item_id
return category_item_id
def addImgItem(file_name, size):
global image_id, id_num
if file_name is None:
raise Exception('Could not find filename tag in xml file.')
if size['width'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find width tag in xml file.')
if size['height'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find height tag in xml file.')
image_item = dict()
# temp = str(id_num)
temp = int(id_num)
# image_item['id'] = image_id + temp
image_item['id'] = temp
id_num += 1
image_item['file_name'] = file_name
image_item['width'] = size['width']
image_item['height'] = size['height']
coco['images'].append(image_item)
image_set.add(file_name)
return image_item['id']
def addAnnoItem(object_name, image_id, category_id, bbox):
global annotation_id
annotation_item = dict()
annotation_item['segmentation'] = []
seg = []
# bbox[] is x,y,w,h
# left_top
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1])
# left_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_top
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1])
annotation_item['segmentation'].append(seg)
annotation_item['area'] = bbox[2] * bbox[3]
annotation_item['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation_item['ignore'] = 0
annotation_item['image_id'] = image_id
annotation_item['bbox'] = bbox
annotation_item['category_id'] = category_id
annotation_id += 1
annotation_item['id'] = annotation_id
coco['annotations'].append(annotation_item)
def parseXmlFiles(xml_path):
for f in os.listdir(xml_path):
if not f.endswith('.xml'):
continue
bndbox = dict()
size = dict()
current_image_id = None
current_category_id = None
file_name = None
size['width'] = None
size['height'] = None
size['depth'] = None
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_path, f)
print(xml_file)
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
if root.tag != 'annotation':
raise Exception('pascal voc xml root element should be annotation, rather than {}'.format(root.tag))
# elem is <folder>, <filename>, <size>, <object>
for elem in root:
current_parent = elem.tag
current_sub = None
object_name = None
if elem.tag == 'folder':
continue
if elem.tag == 'filename':
file_name = elem.text
if file_name in category_set:
raise Exception('file_name duplicated')
# add img item only after parse <size> tag
elif current_image_id is None and file_name is not None and size['width'] is not None:
if file_name not in image_set:
current_image_id = addImgItem(file_name, size)
print('add image with {} and {}'.format(file_name, size))
else:
raise Exception('duplicated image: {}'.format(file_name))
# subelem is <width>, <height>, <depth>, <name>, <bndbox>
for subelem in elem:
bndbox['xmin'] = None
bndbox['xmax'] = None
bndbox['ymin'] = None
bndbox['ymax'] = None
current_sub = subelem.tag
if current_parent == 'object' and subelem.tag == 'name':
object_name = subelem.text
if object_name not in category_set:
current_category_id = addCatItem(object_name)
else:
current_category_id = category_set[object_name]
elif current_parent == 'size':
if size[subelem.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at size tag.')
size[subelem.tag] = int(subelem.text)
# option is <xmin>, <ymin>, <xmax>, <ymax>, when subelem is <bndbox>
for option in subelem:
if current_sub == 'bndbox':
if bndbox[option.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure corrupted at bndbox tag.')
bndbox[option.tag] = int(option.text)
# only after parse the <object> tag
if bndbox['xmin'] is not None:
if object_name is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_image_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_category_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
bbox = []
# x
bbox.append(bndbox['xmin'])
# y
bbox.append(bndbox['ymin'])
# w
bbox.append(bndbox['xmax'] - bndbox['xmin'])
# h
bbox.append(bndbox['ymax'] - bndbox['ymin'])
print('add annotation with {},{},{},{}'.format(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id,
bbox))
addAnnoItem(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id, bbox)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 运行两遍得到训练集、验证集的json文件
xml_path = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ## 原始的xml文件路径
json_file = "YOUR_FILE_PATH" ## 转后保存.json文件的路径
parseXmlFiles(xml_path)
json.dump(coco, open(json_file, 'w'))注意:最后的需要将xml路径和保存json文件路径改成训练集的运行一遍,再改为验证集的运行一遍。
以上内容参考了:目标检测——使用nanodet训练自己制作的数据集并测试模型,通俗易懂(详细图文教程)-CSDN博客
二、文件配置与训练
1、yaml文件修改
将目录config/nanodet_custom_xml_dataset.yml复制一份,另取名作为自己模型的配置文件(笔者这里用config/nanodet_plus-m-416_test.yml),按照一下流程对文件进行修改:
(1).训练后输出文件保存路径save_dir: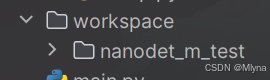 ,里面包含了训练过程的记录、ckpt文件以及训练后的模型
,里面包含了训练过程的记录、ckpt文件以及训练后的模型
(2).训练类别num_classes,根据自己情况修改
(3).类别名称修改:class_names: &class_names ['NAME1', 'NAME2', 'NAME3', 'NAME4', '...'],改为自己类别名如['person']
(4)、训练尺寸和数据集路径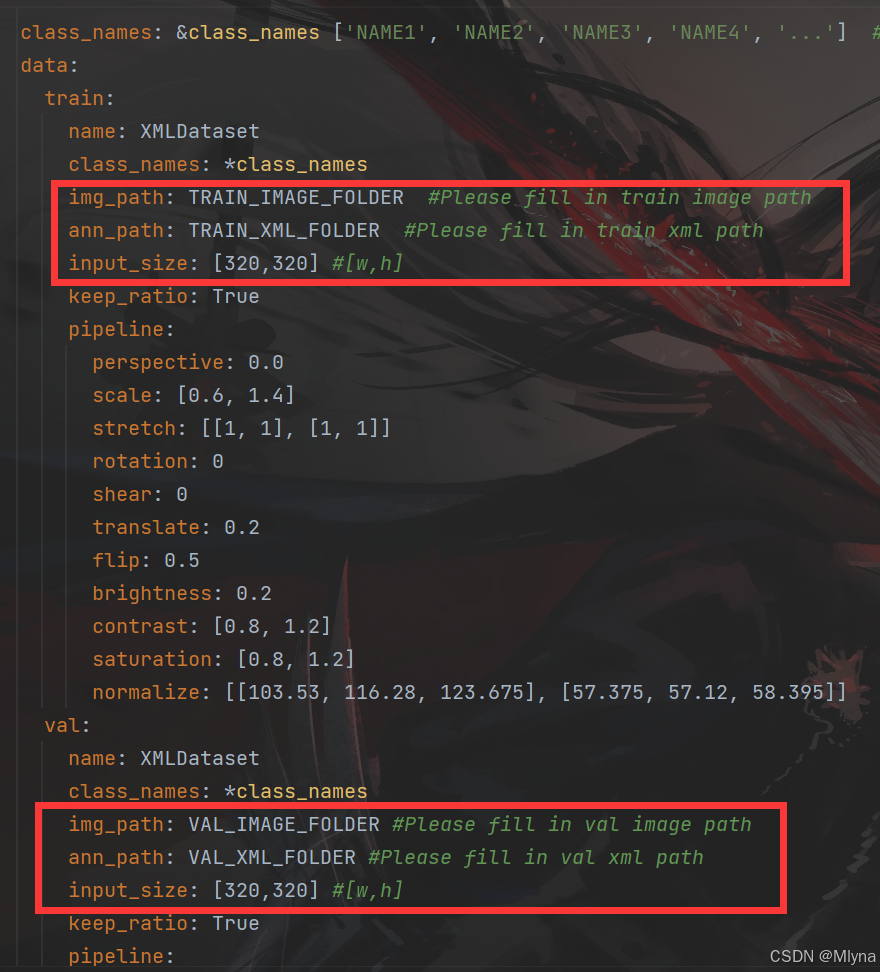
(5)设备改成CPU,既-1,同时修改batchsize、加载模型和轮数epoch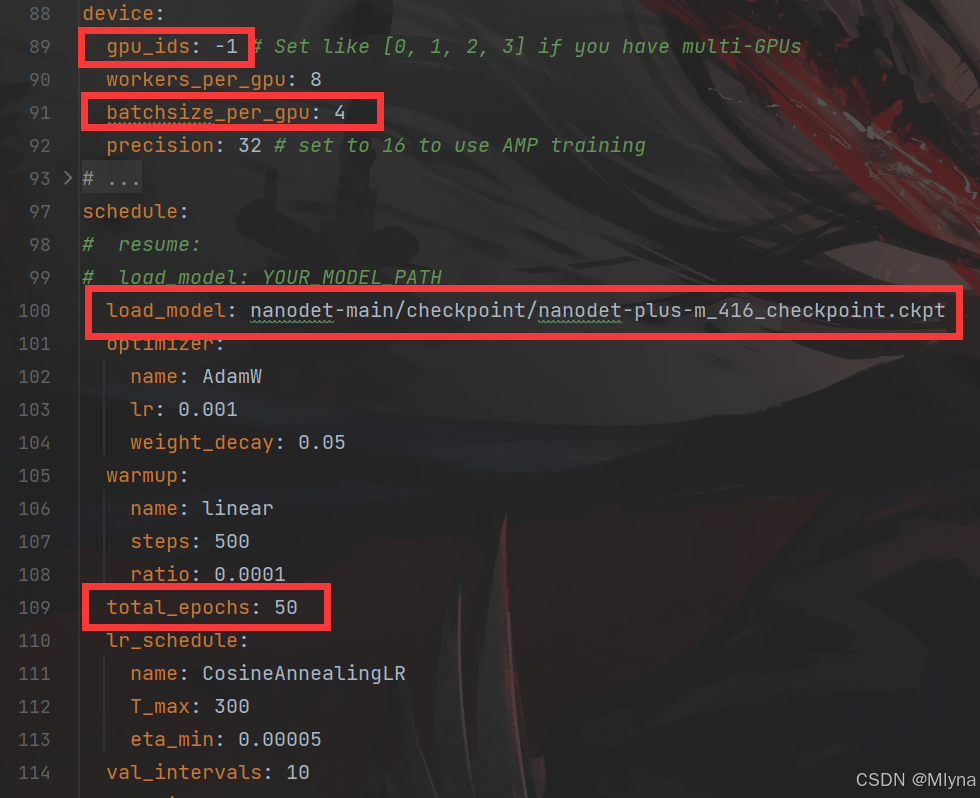
2、train文件修改
torch_load函数加上指定CPU加载模型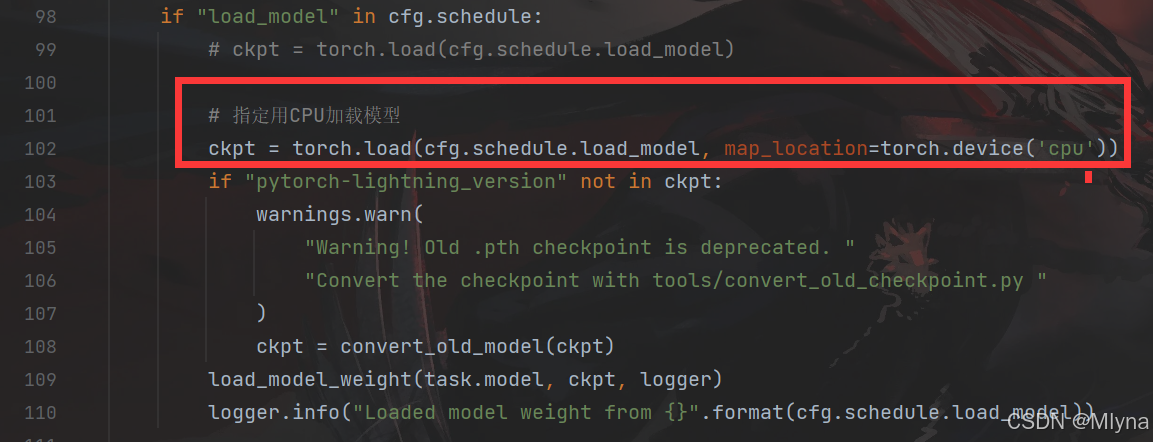
加速器指定为CPU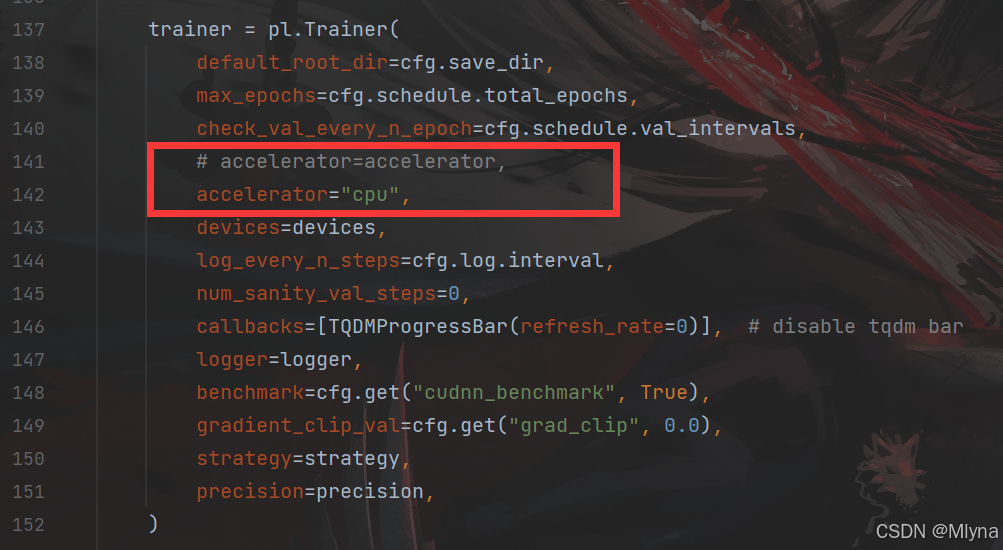
以上内容部分参考了:nanodet-plus训练自己数据集_nanodet训练自己的数据集-CSDN博客,感谢
三、训练
配置好后终端输入:python nanodet-main/tools/train.py nanodet-main/datasets/demo/datasets/medicine/nanodet_plus-m-416_test.yml开始训练。
有以下输出不影响训练,加载时检测到部分参数与模型不匹配所以跳过。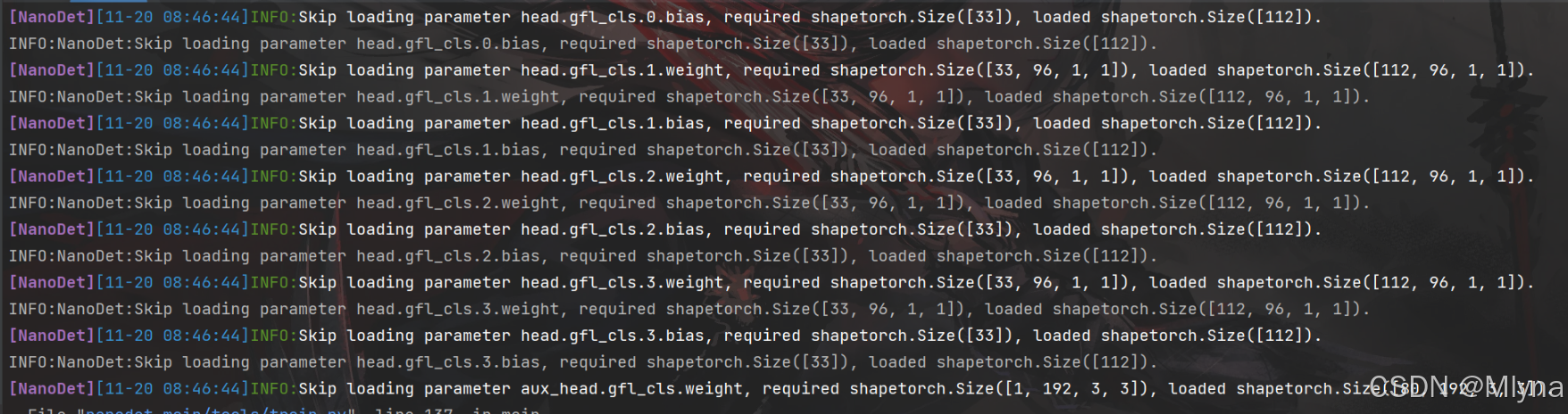
输出一下信息说明开始训练了:
[NanoDet][11-20 10:41:08]INFO:Train|Epoch48/50|Iter3350(61/70)| mem:0G| lr:9.45e-04| loss_qfl:0.0488| loss_bbox:0.1477| loss_dfl:0.1386| aux_loss_qfl:0.0352| aux_loss_bbox:0.1579| aux_loss_dfl:0.1327|
INFO:NanoDet:Train|Epoch48/50|Iter3350(61/70)| mem:0G| lr:9.45e-04| loss_qfl:0.0488| loss_bbox:0.1477| loss_dfl:0.1386| aux_loss_qfl:0.0352| aux_loss_bbox:0.1579| aux_loss_dfl:0.1327|
[NanoDet][11-20 10:41:37]INFO:Train|Epoch49/50|Iter3360(1/70)| mem:0G| lr:9.42e-04| loss_qfl:0.0690| loss_bbox:0.1833| loss_dfl:0.1752| aux_loss_qfl:0.0543| aux_loss_bbox:0.1904| aux_loss_dfl:0.1772|
INFO:NanoDet:Train|Epoch49/50|Iter3360(1/70)| mem:0G| lr:9.42e-04| loss_qfl:0.0690| loss_bbox:0.1833| loss_dfl:0.1752| aux_loss_qfl:0.0543| aux_loss_bbox:0.1904| aux_loss_dfl:0.1772|
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)