python将海康目标检测的打标文件转化成yolo的txt文件
这是海康生成的打标结果,所有结果都放在一个txt文件。其中我拿第一张图片举例。因为yolo的目标检测框数值都在0-1之间,所以需要传入图片原本的大小。其中,需要把你的class更改,还有图片的大小和路径改成自己的。这里1就代表缺焊,0代表正常,是根据代码中的class生成。小tips:图片的像素大小可以查看图片属性的详细信息。
·
其中,需要把你的class更改,还有图片的大小和路径改成自己的。
因为yolo的目标检测框数值都在0-1之间,所以需要传入图片原本的大小。
这是海康生成的打标结果,所有结果都放在一个txt文件。其中我拿第一张图片举例
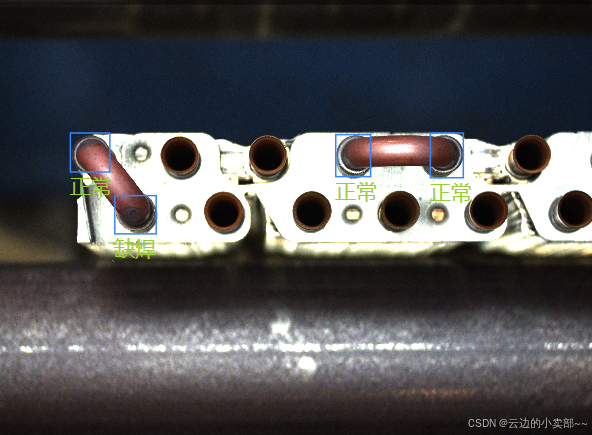
这是海康根据打标结果生成的记录:

这张图片一共有4个检测框,转换为yolo的格式如下:
这里1就代表缺焊,0代表正常,是根据代码中的class生成。

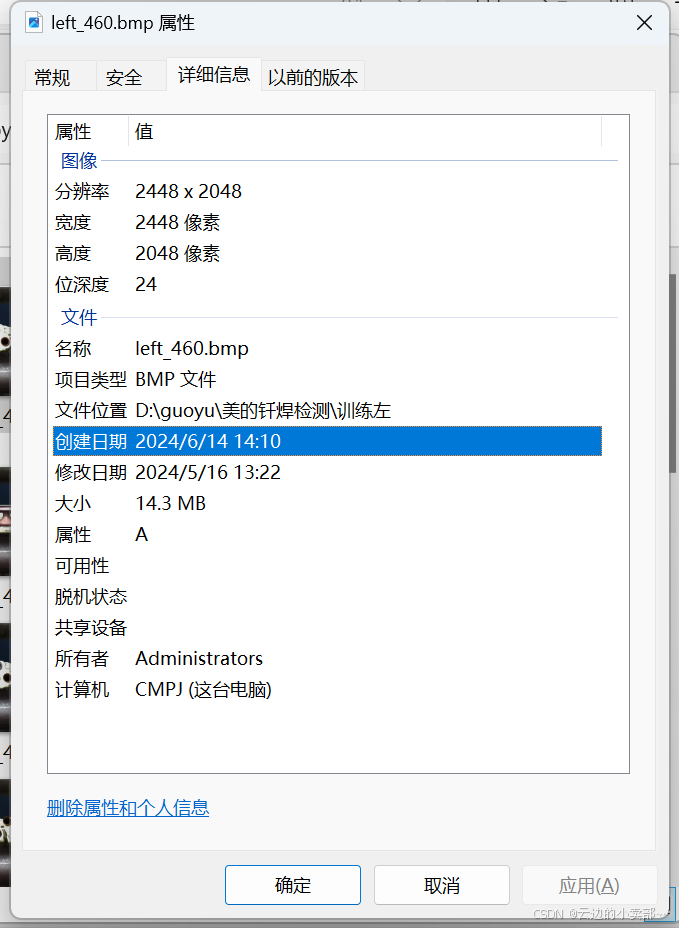
小tips:图片的像素大小可以查看图片属性的详细信息。
完整代码如下:
import os
# 图片的宽度和高度
IMAGE_WIDTH = 2448
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 2048
# 定义分类映射
classification_map = {
"正常": "0",
"缺焊": "1",
"溢焊": "2",
"异常": "3"
}
def normalize(value, max_value):
"""归一化处理,将值缩放到0到1之间"""
return value / max_value
def calculate_center_and_size(coords):
"""计算矩形的中心点、宽度和高度,并归一化处理"""
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = coords
center_x = (x1 + x2 + x3 + x4) / 4
center_y = (y1 + y2 + y3 + y4) / 4
width = max(x1, x2, x3, x4) - min(x1, x2, x3, x4)
height = max(y1, y2, y3, y4) - min(y1, y2, y3, y4)
# 归一化处理
center_x_normalized = normalize(center_x, IMAGE_WIDTH)
center_y_normalized = normalize(center_y, IMAGE_HEIGHT)
width_normalized = normalize(width, IMAGE_WIDTH)
height_normalized = normalize(height, IMAGE_HEIGHT)
return center_x_normalized, center_y_normalized, width_normalized, height_normalized
# 定义输入文件路径和输出文件路径
input_file_path = 'D:\guoyu\美的钎焊检测\训练左\DetectTrainData.txt' # 替换为你的输入文件路径
output_directory = 'D:\guoyu\美的钎焊检测\label' # 替换为你的输出文件目录
# 创建输出目录(如果不存在的话)
os.makedirs(output_directory, exist_ok=True)
# 打开并读取原始文件
with open(input_file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
# 逐行读取文件内容
for line in file:
# 去除每行末尾的换行符
line = line.strip()
# 如果行内容非空,则处理该行
if line:
# 分割行内容,提取第一个部分作为文件名
parts = line.split(':')
if parts:
file_name = parts[0].split('.')[0] # 去掉文件扩展名
output_file_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'{file_name}.txt') # 生成新的文件名路径
# 打开新的文件进行写入
with open(output_file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as output_file:
# 以 ' R:' 分割每一部分
segments = line.split(' R:')
for segment in segments[1:]:
# 去除每个 segment 的前导和尾随空白字符,并分割成部分
segment_parts = segment.strip().split()
# 检查 segment_parts 长度是否足够
if len(segment_parts) < 10:
print(f"警告:segment_parts 长度不足,内容为:{segment_parts}")
continue
# 提取分类标签(最后一个部分去掉双引号)
classification_label = segment_parts[-1].strip('"')
# 根据分类标签获取相应的数字
classification_number = classification_map.get(classification_label, "未知分类")
# 提取坐标部分,并确保其可以被正确转换为整数
try:
coords = list(map(int, segment_parts[1:9]))
except ValueError as e:
print(f"错误:无法转换坐标部分为整数,segment_parts 为:{segment_parts[1:9]}")
continue
# 计算中心点、宽度和高度,并归一化
center_x, center_y, width, height = calculate_center_and_size(coords)
# 写入分类数字
output_file.write(classification_number + " ")
# 写入归一化后的中心点和宽度、高度
output_file.write(f"{center_x:.6f} {center_y:.6f} {width:.6f} {height:.6f}\n")
print("文件处理完成。")
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)