【论文阅读】一种基于时间序列的 FL 节省算力被动成员推断攻击 Efficient passive membership inference attack in federated learning
相较于之前的目录
来源论文:Efficient passive membership inference attack in federated learning
相较于之前基于更新量的成员推断攻击,本文提出一种黑盒的利用 连续次更新量(结合了 time series) 的 推断攻击,仅需 极小的计算量(虽然攻击准确率差不多)。
Threat model:被动成员推断攻击
假设在 FL 中,Server 或者 某一位 client 为攻击者,要对某一个 client 的 targer model 作成员推断攻击,攻击者可以获取到 target model 的以下信息:1.该模型所有轮上传的参数,并且根据这个参数,可以获取 target model 后几层的输出。2.辅助数据集,要求和代攻击的数据集同分布,用于训练 target model。
Methodology
按照传统的利用 模型后几层 对 input 的 梯度 的推断方法,会导致:
For instance, to achieve the attack on FL training of AlexNet on CIFAR100, the adversary computes 5 × 20000 gradients [9, Table XI and XII], which takes at least 1.5 hours on a NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti.
由此可见,针对复杂模型,需要计算大量神经元的梯度,
所以本文提出的方法,索性不用模型内部信息了,直接用 prediction vector 来做(每一个类别的概率)。
比如,在 30 轮 连续获取到的 target model ,对 某一条 待验证成员信息的数据进行预测,得到 维度为 30 × c l a s s e s _ n u m 30 \times classes\_num 30×classes_num 的矢量,这一堆二维矢量作为 attack model 的输入,来看一下 attack model 的结构: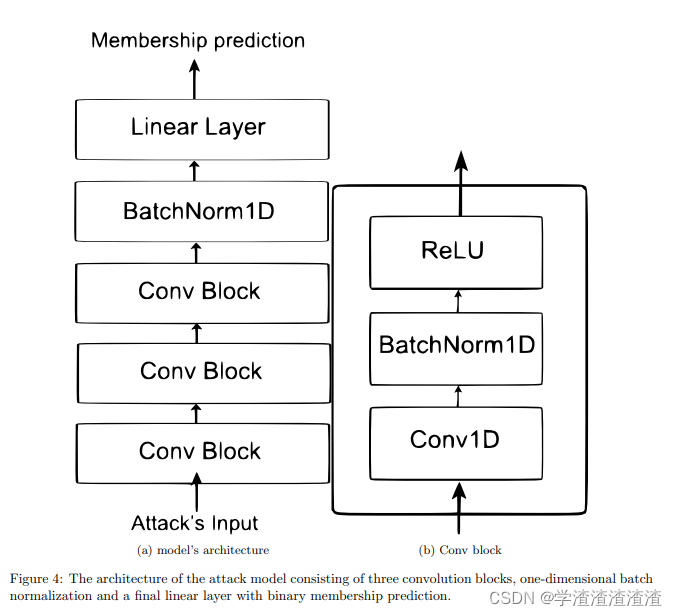
来看一下作者解释为什么要这么做:
Also the attack model architecture in [9] considers the input as a flat vector, while our architecture is designed to explicitly capture the FL training dynamics, which may expose more information about data point’s membership.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容






所有评论(0)